Inguinal hernia is a common medical condition that occurs when soft tissues, usually part of the intestine, protrude through a weak point or tear in the lower abdominal wall. It is the most common type of hernia and affects both men and women, although it is more frequently found in men. In this article, we will delve into the causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, home remedies, and some frequently asked questions about inguinal hernias.
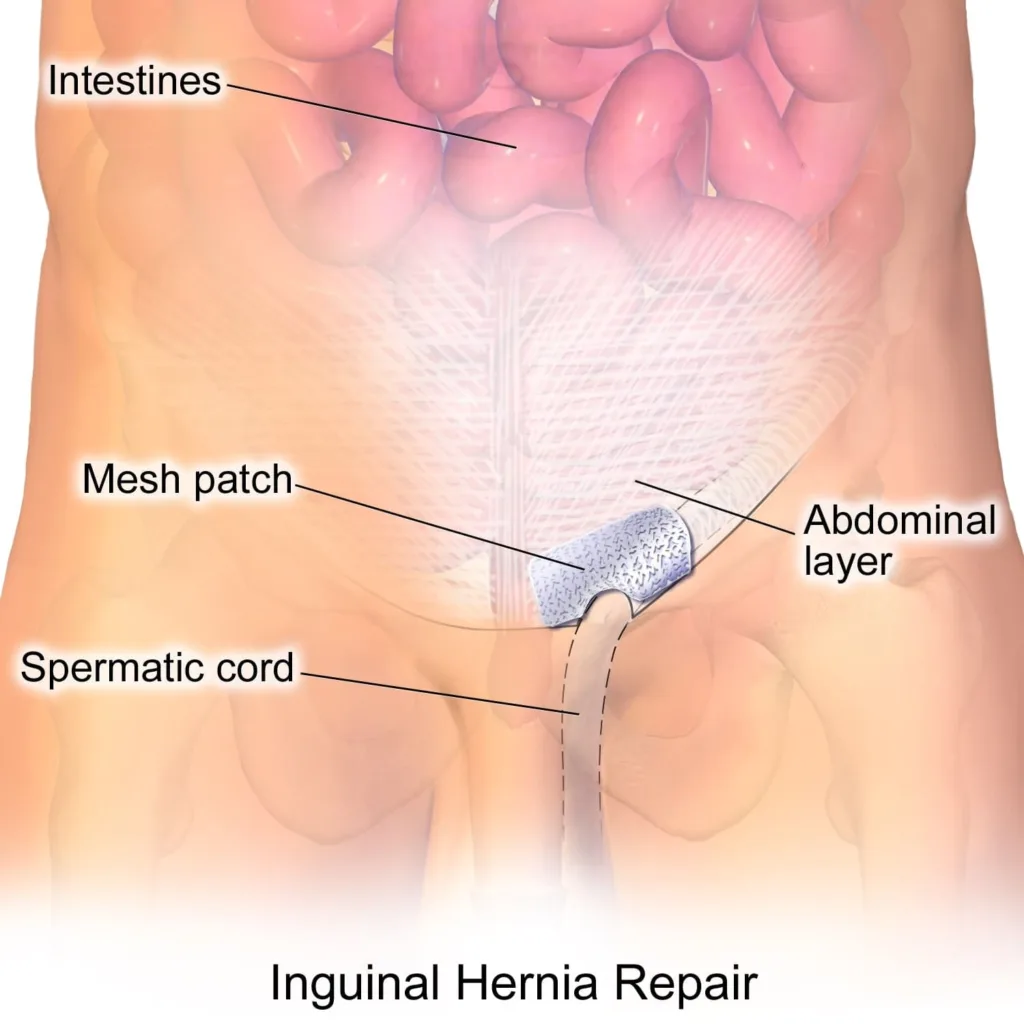
How Common is Inguinal Hernia?
Inguinal hernias are quite common, with millions of cases diagnosed worldwide each year. Men are more likely to develop this condition, with the peak incidence occurring in middle-aged and older individuals. It is estimated that up to 25% of men and 2% of women will experience an inguinal hernia at some point in their lives.
Causes of Inguinal Hernia
The main cause of inguinal hernias is a weakness in the abdominal wall, which can be present at birth or acquired later in life. Some common factors that contribute to the development of the condition include:
Increased abdominal pressure: Heavy lifting, persistent coughing, obesity, chronic constipation, or straining during urination can create pressure on the abdominal wall, leading to hernia formation.
Muscle weakness: Certain individuals may have a congenital weakness in the abdominal wall, making them more prone to developing an inguinal hernia.
Age and gender: The risk of developing an inguinal hernia increases with age and is more prevalent in males due to the natural structure of the male groin area.
Types of Inguinal Hernia
There are two primary types of inguinal hernias:
Indirect inguinal hernia: This is the most common type of inguinal hernia and occurs when the small intestine protrudes through a weak spot in the inguinal canal, which is a passageway in the groin area that houses the spermatic cord in men.
This is the most prevalent form, and you may be born with it. Although it may occur in both men and women, it is far more prevalent in men. This is due to the fact that the male testicle begins inside the belly and must descend via a groin hole to reach the scrotum (the sac that houses the testicles). A hernia forms if this opening does not close at birth. This form of hernia can arise in women if the reproductive organs or the small intestine move into the groin region due to a weakening in the abdominal muscles
Direct inguinal hernia: This type of hernia is more common in older adults and occurs when the intestine pushes through a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall.
Symptoms of Inguinal Hernia
Symptoms
Groin enlargement or swelling
When standing, coughing, or straining, the bulge becomes more visible.
When laying down, the lump may vanish.
Groin discomfort or a dragging feeling
Aching or pain in the groin, particularly during vigorous exertion or when carrying large goods
Feelings of groin pressure or weakness
Burning or intense pain at the hernia location
Complications such as bowel blockage or strangulation are rare but can result in severe discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and difficulty to pass stool or gas.
It’s crucial to understand that not everyone who has an inguinal hernia will have symptoms. If any of these symptoms appear, it is critical to get medical attention for correct diagnosis and treatment.
Of all the above symptoms the most common and prominent ones are the following :
Visible bulge:
A noticeable bulge or swelling in the groin area is usually the most apparent symptom.
Pain or discomfort: Discomfort or aching may be felt, especially when lifting heavy objects, coughing, or bending over.
Burning or pressure:
Some individuals may experience a burning sensation or pressure in the affected area.
Weakness or heaviness:
A feeling of weakness or heaviness in the groin can also be present.
Symptoms In Children
Inguinal hernias in neonates and children are caused by a congenital defect in the abdominal wall. When an infant is screaming, coughing, or straining during a bowel movement, the hernia may be evident. He or she may be irritated and eat less than normal.
A hernia in an older kid is more likely to be seen when the youngster coughs, stretches during a bowel movement, or stands for an extended amount of time.
Who Is At A Greater Risk :
The following factors lead to the development of an inguinal hernia:
Being a man. Men are eight times more likely than women to acquire an inguinal hernia.
Growing older. Muscles deteriorate with ageing.
Being a white person.
A family tree. You have a close family with the illness, such as a parent or brother.
Smoking causes a chronic cough.
Constipation that lasts a long time. Constipation causes bowel motions to be strained.
Pregnancy. Pregnancy can cause abdominal muscular weakness and increased pressure inside the abdomen.
Low birth weight and premature birth. Premature or low birth weight newborns are more likely to have inguinal hernias.
Complications Of Inguinal Hernia
Increased Pressure on Surrounding tissues : Most inguinal hernias grow over time if not surgically fixed. Large hernias in males can cause discomfort and swelling in the scrotum.
Incarcerated Hernia: If the contents of the hernia become stuck in the weak area in the abdominal wall, they can clog the intestine, causing extreme discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and the inability to pass gas or have a bowel movement.
Strangulation: A hernia that has become entrapped might shut off blood supply to a portion of your intestine. The damaged intestinal tissue may die as a result of strangulation. A strangulated hernia is potentially fatal and need prompt surgery.
Diagnosis of Inguinal Hernia
Inguinal hernia diagnosis is typically performed through a combination of physical examination and medical imaging techniques. During a physical examination, a healthcare professional will carefully evaluate the patient’s groin area to look for signs of a hernia. This may involve feeling for any bulges or lumps that appear when the patient coughs or strains. The healthcare provider will also take note of any symptoms reported by the patient, such as pain, discomfort, or a dragging sensation in the groin region. Additionally, the medical professional may ask the patient to stand up and bear down to further assess the presence of a hernia.
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the exact location and size of the hernia, medical imaging tests may be recommended. One commonly used technique is ultrasound imaging, which uses high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of the internal structures. Ultrasound can help visualize the hernia sac, its contents, and the surrounding tissues.
In some cases, other imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be utilized to provide a more comprehensive view of the hernia and assess any complications or associated conditions.
It is important to note that in certain cases, an inguinal hernia may not be easily detected during a physical examination. This is referred to as a “hidden” or “occult” hernia. In such situations, additional diagnostic tests, such as a dynamic MRI or laparoscopy, may be necessary to accurately diagnose the condition.
Overall, a combination of physical examination and medical imaging techniques is crucial for the accurate diagnosis of an inguinal hernia. These diagnostic tools help healthcare professionals assess the location, size, and severity of the hernia, guiding them in determining the most appropriate treatment approach for each individual patient.
Preventive Measures
You cannot avoid the congenital abnormality that predisposes you to an Inguinal Hernia. However, you can lessen the tension on your abdominal muscles and tissues. As an example:
Keep a healthy weight. Consult your doctor to determine the appropriate workout and nutrition plan for you.
High-fiber foods should be prioritized. Fibre found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help avoid constipation and straining.
Lift big things with caution or avoid heavy lifting altogether. If you must lift something heavy, always bend from the knees rather than the waist.
Quit smoking. Aside from its role in many severe illnesses, smoking frequently produces a persistent cough, which can lead to or worsen an inguinal hernia.
Home Remedies for Inguinal Hernia
While home remedies cannot cure an inguinal hernia, they can help alleviate symptoms and provide temporary relief. Here are a few suggestions:
Supportive garments: Wearing supportive underwear or using a truss can help reduce discomfort by providing gentle compression to the area.
Avoid heavy lifting: Minimize activities that require excessive strain on your abdominal muscles.
Maintain a healthy weight: Losing excess weight can decrease pressure on the abdomen and reduce symptoms.
Dietary changes: Avoiding foods that cause constipation can help prevent straining during bowel movements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can an inguinal hernia go away on its own?
No, inguinal hernias do not resolve on their own and typically require surgical intervention.
Is surgery the only treatment option for an inguinal hernia?
Surgery is the most effective and commonly recommended treatment for inguinal hernias; however, your doctor may suggest watchful waiting for small hernias that are not causing significant symptoms.
Can I exercise with an inguinal hernia?
It is best to consult with your healthcare provider before engaging in physical activities if you have an inguinal hernia. They can provide guidance based on your specific condition.
Are there any complications associated with untreated inguinal hernias?
If left untreated, inguinal hernias can lead to severe complications such as bowel obstruction or strangulation, where blood supply to the herniated tissues is cut off.
Remember, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment options if you suspect you have an inguinal hernia.
Reference : http://www.webmd.com







