Testosterone is a vital hormone for both men and women, but it plays a particularly important role in men’s health. It influences muscle mass, bone density, sex drive, and mood, among other things. Unfortunately, many men experience a decline in testosterone levels as they age, leading to a variety of unwanted symptoms and health concerns. This blog post will delve into the importance of testosterone, the causes and symptoms of deficiency, and scientifically backed ways to naturally boost testosterone levels.
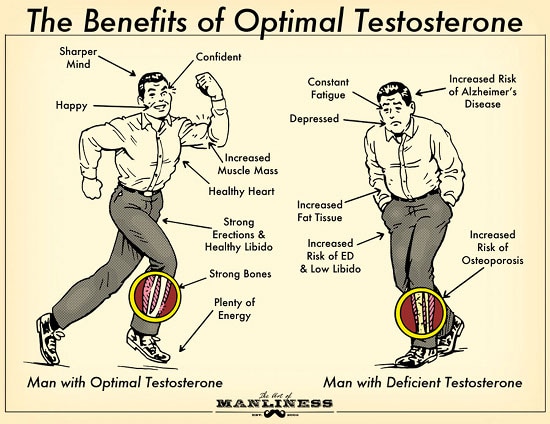
Why Testosterone is Important
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone, but it also exists in small amounts in women. It’s produced mainly in the testes for men and the ovaries and adrenal glands in women. Testosterone has a variety of key functions:
Muscle Mass and Strength: It stimulates muscle growth and is one of the reasons why men tend to have more muscle mass than women.
Bone Density: It plays a crucial role in maintaining bone strength and density.
Sex Drive and Reproduction: Testosterone influences libido, sperm production, and overall sexual function.
Mood and Energy: Balanced testosterone levels help maintain a healthy mood, emotional stability, and energy levels.
Cognitive Function: Testosterone has been shown to support memory, focus, and cognitive function.
As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline. This process starts around age 30 and continues throughout a man’s life. While this decline is gradual, some men may experience more significant drops in testosterone, which can lead to various symptoms and health issues.
Causes of Testosterone Deficiency
Testosterone deficiency, also known as hypogonadism, can be caused by a variety of factors, both external and internal. The following are the most common causes:
Aging: Natural aging leads to a slow and steady decline in testosterone levels.
Obesity: Excess body fat, particularly around the belly , is indicative of lower testosterone levels. Fat cells convert testosterone into estrogen, further reducing levels of the hormone.
Chronic Stress: Prolonged stress increases cortisol, a hormone that can reduce testosterone production when chronically elevated.
Poor Diet: Diets high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can contribute to hormonal imbalances.
Lack of Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle can result in reduced testosterone levels, particularly in those who don’t engage in strength training or high-intensity exercises.
Sleep Deprivation: Inadequate sleep, particularly REM sleep, has been linked to lower testosterone levels.
Medical Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, liver or kidney disease, and pituitary gland issues can contribute to low testosterone levels.
Alcohol and Drug Abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption and certain drugs can negatively affect testosterone production.
Symptoms of Low Testosterone
Low testosterone levels can manifest in a variety of symptoms, which can sometimes be mistaken for other health issues. Recognizing these signs is the first step toward addressing a potential deficiency. Common symptoms include:
Fatigue: Chronic low energy levels, even after a full night’s sleep.
Decreased Libido: A reduced interest in sex or difficulties with sexual performance.
Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
Muscle Loss: A noticeable decline in muscle mass and strength.
Increased Body Fat: Particularly around the abdomen, along with difficulty losing weight.
Mood Swings: Increased irritability, depression, or anxiety.
Reduced Cognitive Function: Trouble concentrating, memory problems, or lack of mental clarity.
Osteoporosis: Weak or brittle bones in severe cases of long-term deficiency.
Hair Loss: A reduction in facial or body hair.
If left untreated, long-term testosterone deficiency can lead to more serious conditions such as heart disease, osteoporosis, and metabolic syndrome. Fortunately, there are natural ways to boost testosterone levels without the need for hormone replacement therapy or medications.
Natural Ways to Boost Testosterone
Exercise Regularly
It has been demonstrated that physical activity raises testosterone levels, especially strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT). Exercises involving weightlifting, such as bench presses, deadlifts, and squats, are very beneficial. Strength training contributes to the growth of muscular mass, which increases the production of testosterone. Short bursts of intensive exercise followed by rest, or HIIT exercises, have also been demonstrated to raise hormone levels.
It’s important to avoid overtraining, as excessive exercise can raise cortisol levels, which can negatively impact testosterone.
Get Enough Quality Sleep
Sleep is crucial for hormone regulation, and testosterone is no exception. During deep sleep (REM sleep), the body produces the most testosterone. Research shows that individuals who get less than 5 hours of sleep per night may experience a 10-15% reduction in testosterone levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to ensure optimal hormonal function.
To improve sleep quality, establish a regular sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and minimize screen time before bed. your sleeping environment should be quiet, comfortable, cool, and dark.
Maintain a Balanced Diet
Nutrition plays a key role in maintaining healthy testosterone levels. The various minerals you need to focus on and must include in your diet are : :
Protein: Protein is essential for muscle building, which can indirectly boost testosterone. Lean meats, fish, eggs, and plant-based proteins are great options.
Healthy Fats: Healthy fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, have been shown to support testosterone production. Include sources such as avocados, olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish like salmon in your diet.
Carbohydrates: Carbs are necessary for energy, and low-carb diets can sometimes reduce testosterone levels. Choose complex carbs such as those found in veggies, legumes, and whole grains.
Micronutrients: The synthesis of testosterone depends on a number of vitamins and minerals. These include zinc (found in oysters, beef, and pumpkin seeds) and vitamin D (found in fatty fish, fortified foods, and sunlight exposure).
Reduce Stress
Chronic stress increases the production of cortisol, a hormone that can inhibit testosterone production. Finding ways to manage and reduce stress is key to maintaining healthy hormone levels. One can use variety of measures such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help lower stress levels. Additionally, engaging in regular physical activity and ensuring adequate rest and relaxation can be beneficial.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, can lead to lower testosterone levels. Fat cells convert testosterone into estrogen, a female hormone, which further reduces testosterone levels. By maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise, you can help balance hormone levels and promote overall well-being.
Take Natural Supplements
Several natural supplements have been shown to support testosterone production. These include:
Ashwagandha: This adaptogenic herb has been used in traditional medicine to reduce stress and increase testosterone levels.
Fenugreek: Some studies suggest that fenugreek can increase testosterone levels and improve sexual function.
Ginger: Ginger is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and may also help boost testosterone production.
DHEA: Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is a hormone precursor that the body can convert into testosterone. While more research is needed, some studies suggest that DHEA supplementation may be beneficial for increasing testosterone.
Before taking any supplements, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider, especially if you’re taking other medications or have underlying health conditions.
Limit Alcohol and Avoid Drug Use
Excessive alcohol consumption has been shown to reduce testosterone levels. Alcohol can increase the production of cortisol and inhibit the release of testosterone. Moderate alcohol consumption, such as a glass of wine or beer occasionally, is generally not harmful, but excessive drinking can lead to long-term hormonal imbalances.
Additionally, the use of recreational drugs, including marijuana and anabolic steroids, can interfere with the body’s natural testosterone production and should be avoided.
Stay Hydrated
Hydration is often overlooked in discussions about hormonal health, but dehydration can impact physical performance, energy levels, and testosterone production. Drinking enough water throughout the day is essential for overall health and hormone balance.
Sunlight and Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a crucial nutrient for testosterone production, and sunlight is one of the best sources. Spending 15-30 minutes outside each day, especially during midday when the sun is strongest, can help increase your body’s natural production of vitamin D. If sunlight exposure is limited, consider taking a vitamin D supplement to support testosterone levels.
Cold Showers
While more research is needed, some studies suggest that cold exposure, such as cold showers or ice baths, may help stimulate testosterone production. Cold showers can also reduce inflammation, improve circulation, and boost energy levels—all of which may indirectly support healthy hormone levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can testosterone levels be too high?
Yes, excessively high testosterone levels can lead to health problems such as mood swings, aggression, acne, and sleep disturbances. It can also increase the risk of heart disease in some cases. It’s essential to aim for a balanced level of testosterone, neither too high nor too low.
2. How do I figure out if I am low on testosterone?
Common symptoms of low testosterone include fatigue, reduced libido, muscle loss, mood changes, and weight gain. A blood test is the most accurate way to measure testosterone levels, and your healthcare provider can help interpret the results.
3. At what age does testosterone naturally decline?
Testosterone levels begin to ebb out gradually after the age of 30. This decline is usually slow, but some men may experience more noticeable symptoms as they age.
4. Can women have low testosterone?
Yes, women also produce testosterone, though in smaller amounts than men. Low testosterone in women can result in symptoms such as fatigue, reduced libido, muscle weakness, and mood changes. Women experiencing these symptoms should consult with their healthcare provider to assess hormone levels and explore potential treatments.
5. Are natural testosterone boosters safe?
Most natural testosterone boosters, like dietary changes, exercise, sleep improvement, and stress reduction, are generally safe and beneficial for overall health. However, supplements should be used with caution. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially if you have existing medical conditions or take other medications.
6. How long does it take to see results from natural testosterone-boosting methods?
The timeframe for seeing results varies depending on the individual and the methods being used. For example, improvements from exercise and dietary changes may become noticeable within a few weeks, while the effects of supplements or lifestyle changes like improved sleep may take longer to manifest. Consistency is key for long-term results.
7. Can stress really lower testosterone levels?
Yes, chronic stress can elevate cortisol levels, which can interfere with testosterone production. Managing stress through techniques like meditation, mindfulness, exercise, and adequate rest is crucial for maintaining healthy testosterone levels.
8. Is testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) better than natural methods?
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is a medical treatment for those with clinically low testosterone levels that don’t respond to natural methods. While TRT can be highly effective, it also comes with potential risks and side effects, such as increased risk of heart disease and infertility. Natural methods of boosting testosterone are often preferred as a first-line approach because they come with fewer risks and have broader benefits for overall health.
9. Does weight loss affect testosterone levels?
Yes, losing weight, especially excess body fat, can help increase testosterone levels. This is because fat cells convert testosterone to estrogen, and having too much body fat can disrupt hormone balance. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight are key strategies for supporting testosterone levels.
10. Can low testosterone levels affect fertility?
Low testosterone can impact fertility by reducing sperm production and sexual function. However, testosterone therapy is not typically used to treat infertility, as it can sometimes worsen sperm production. Men facing fertility issues should seek advice from a healthcare provider specializing in reproductive health.
Conclusion
Testosterone plays a critical role in many aspects of health, from physical strength and sex drive to mental well-being. Maintaining optimal testosterone levels, particularly as you age, is key to feeling and performing your best. Fortunately, there are many natural ways to support testosterone production, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management. By making these changes, you can improve your overall health and enhance your testosterone levels naturally.
For those with significant symptoms or concerns about low testosterone, it’s important to seek advice from a healthcare provider, who can help guide you toward appropriate testing and treatment options. Whether through natural methods or medical intervention, taking action to maintain healthy testosterone levels is a step toward improved vitality and longevity.
Disclaimer : This article is only for educational purposes. Please consult a medical practitioner before using any bit of information from the article in your life.
Reference : http://www.mayoclinic.org







